What is Social Structure: Uncovering the Pattern of Society
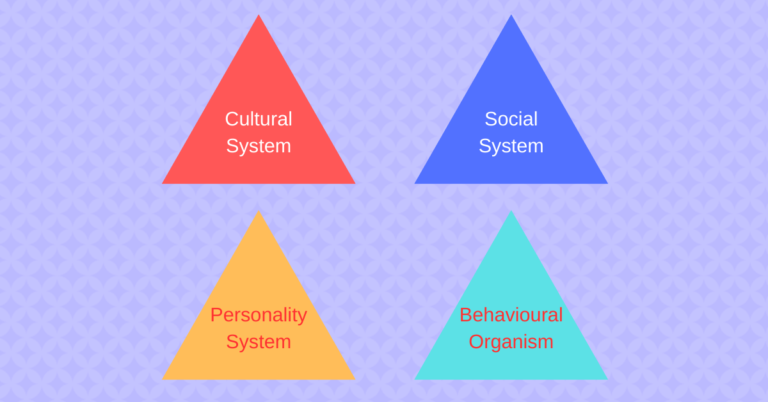
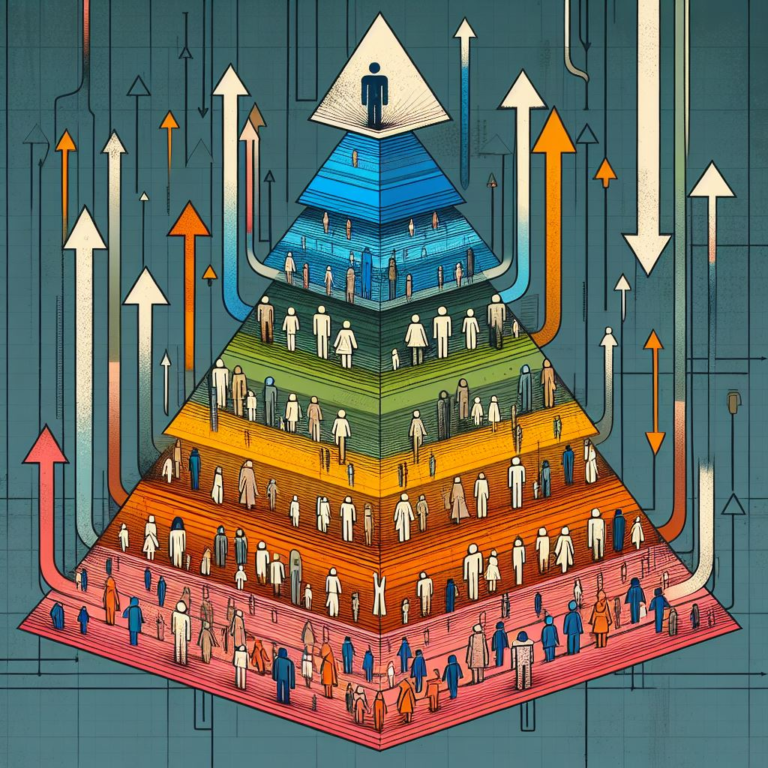
Understanding Social Structure Social structure refers to the enduring patterns of social relationships, institutions, and practices that exist within a society. It includes the organized and recurrent arrangements of power, status, and resources within a society. Social structure refers to the way that social institutions, such as the family, education, religion, and government, are organized […]